Introduction
Enterprise-scale content migrations are far more complex than simple file transfers — they require automation, governance, and intelligence.
This post shares how we migrated SharePoint-hosted agency/department websites into a unified Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) platform — a massive consolidation effort involving over hundreds of thousands of documents and tens of thousands of content pages.
The focus here is on the technical implementation, automation pipelines, and AI integration that made this possible.
Step 1: Discovery & Analysis
Technical Audit
- Mapped a large number of SharePoint subdomains (e.g.,
department1.site.com,department2.site.com). - Extracted site metadata and content structures using SharePoint REST APIs.
- Identified document libraries, embedded assets, and internal navigation dependencies.
Content Audit
- Classified content types: services, policies, FAQs, announcements, and forms.
- Flagged outdated or duplicated material.
- Conducted stakeholder workshops across agencies to capture content priorities.
Step 2: Build Custom Migration Utilities
There’s no direct tool to migrate content from SharePoint to AEM — so we developed a custom ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline.
2.1 Extraction (Python + SharePoint REST API)
We extracted data using Python and the SharePoint REST endpoints:
import requests
def extract_content(site_url, list_name, access_token):
endpoint = f"{site_url}/_api/web/lists/getbytitle('{list_name}')/items"
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}", "Accept": "application/json;odata=verbose"}
response = requests.get(endpoint, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()['d']['results']
Features:
- Incremental extraction using modified timestamps.
- Recursive folder and subsite traversal.
- JSON metadata output for transformation.
2.2 Transformation
All SharePoint content was normalized into AEM-compatible JSON schemas.
def transform_to_aem_format(item, agency):
return {
"jcr:primaryType": "cq:Page",
"jcr:title": item["Title"],
"body": sanitize_html(item.get("Body", "")),
"cq:tags": [f"state:agency/{agency.lower()}"],
"publishDate": item["Created"],
"sourceSystem": "SharePoint",
"migratedBy": "MigrationBot"
}
Enhancements:
- Sanitized HTML to remove legacy SharePoint markup.
- Preserved author, creation date, and metadata.
- Injected tag namespaces and structured taxonomy.
2.3 Upload to AEM
Used the Sling POST Servlet and AEM Assets HTTP API to import transformed content:
curl -u admin:admin \
-F "file=@content.json" \
-F "jcr:primaryType=nt:file" \
https://state.com/api/assets/content/agency/health/
Pipeline Features:
- Parallel uploads with retry logic.
- Checksum validation for every upload.
- Logging of source-target mappings.
Step 3: Restructure Site Architecture
Before: https://department.sharepoint.com
After:
https://sharepoint.com/department/<department-name>https://sharepoint.com/services/<service-name>
Outcome:
- Consistent design and content governance.
- Better SEO performance.
- Unified navigation experience.
Step 4: Metadata & Tagging
Technical Implementation
- Tag namespaces:
site:agency,site:services,topic,audience - Automated tag assignment during transformation
- Embedding tags into AEM templates
Example Tag Matrix
| Title | Tags |
|---|---|
| Renew Driver’s License | site:departments/transport, site:services/driver-license |
| COVID-19 Resource Guide | site:agency/medical, topic:public-health, audience:residents |
AI Tagging
- Smart tagging via AEMaaCS
- Contextual tags for unstructured content
Architecture Overview
The following diagram illustrates the end-to-end technical workflow implemented during the migration:
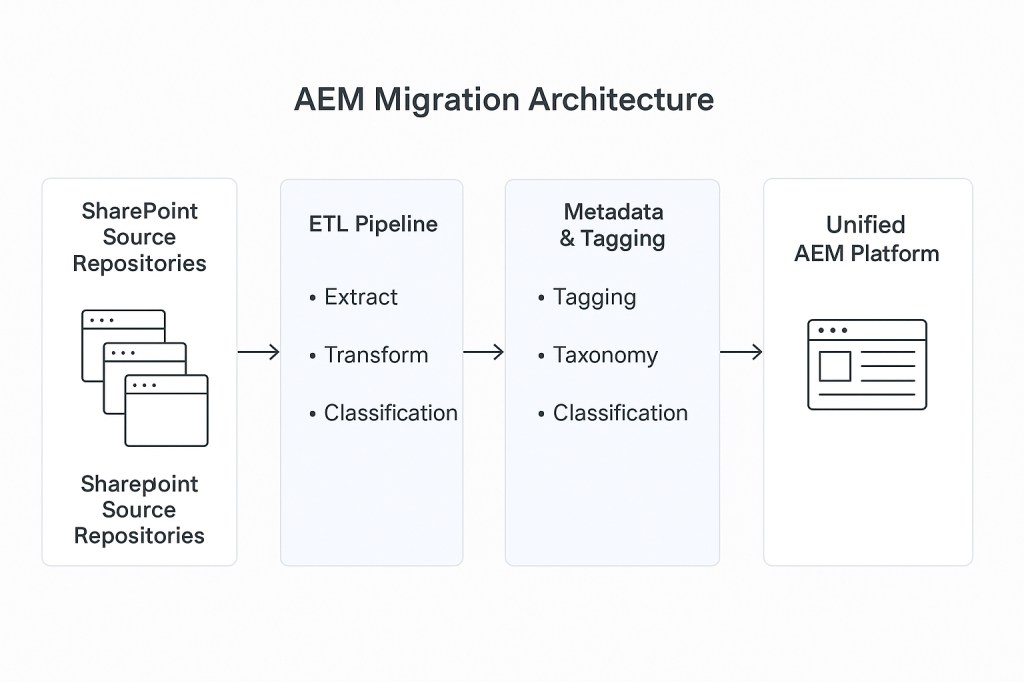
Architecture Layers
- SharePoint Source Repositories: Unique content sites.
- ETL Pipeline: Python-based utilities for extraction, transformation, and load.
- Metadata & Tagging: AI-driven tagging with controlled vocabulary enforcement.
- Quality Assurance: Validation for accessibility, SEO, and link integrity.
- Unified AEM Platform: Consolidated site with reusable components and templates.
Step 5: Batch Migration & Automation
- CLI pipeline:
Extract → Transform → Tag → Upload → Validate - Batch size: 5–8 agencies per wave, ~2–3 weeks each
- Automated QA: checksum validation, content diff reports, tag coverage dashboards
This automation pipeline handled each agency migration batch efficiently.
Automation Steps
- Extract – Pull metadata and assets from SharePoint.
- Transform – Convert content into AEM-compatible JSON.
- Tag – Assign metadata and topic tags.
- Upload – Push data to AEM using API endpoints.
- Validate – Perform QA and checksum verification.
Each batch processed 5–8 agencies, with full QA reports generated automatically.
Step 6: QA & Optimization
Technical QA
- Link integrity checks across numerous sites
- Lighthouse performance audits
- Browser and device testing
Content QA
- Accessibility (WCAG 2.1 AA)
- Editorial review in staging
- SEO optimization (titles, meta descriptions, canonical URLs)
Results
| Outcome | Metric / Benefit |
|---|---|
| Unified AEM Platform | Dozens of agencies, Tens of thousands of pages, 250k assets consolidated |
| Search & Discoverability | 30% improvement |
| Metadata Governance | Standardized tagging, controlled vocabulary |
| Editorial Efficiency | Reusable templates and components |
| Resident Experience | Consistent UX and navigation |
Key Takeaways
- Plan metadata and taxonomy before migration
- Batch agencies logically based on readiness
- Automate extraction, transformation, and QA
- Use AI for tagging, clustering, and summarization
- Governance and version control are essential
Leave a comment